Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, search engine optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role in ensuring online visibility and driving organic traffic to websites. One often overlooked but essential aspect of SEO is the proper utilization of XML sitemaps. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of XML sitemaps in SEO and how they can help websites achieve better rankings on search engine result pages (SERPs).

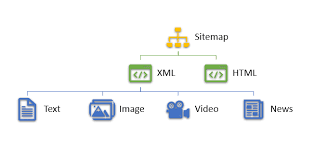
What is an XML Sitemap?
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the URLs of a website and provides essential information about each page, such as when it was last updated, its priority, and the frequency of changes. This file acts as a roadmap for search engine crawlers, helping them discover and index web pages more efficiently. By submitting an XML sitemap to search engines, website owners can ensure that their content is crawled and indexed accurately.
Also Check SEO for E-commerce Product Pages: Best Practices 2023
Benefits of XML Sitemaps for SEO
1. Improved Crawling and Indexing
XML sitemaps serve as a direct line of communication between website owners and search engines. By providing a clear and structured overview of a website’s pages, XML sitemaps make it easier for search engine bots to navigate and understand the site’s content. This ultimately leads to more efficient crawling and indexing, ensuring that all relevant pages are included in search engine databases.
2. Enhanced Visibility
When search engines understand the structure and content of a website better, they can present it to users in a more targeted and relevant manner. XML sitemaps facilitate this process by providing additional metadata about each page, such as its priority and the frequency of updates. By including this information, website owners can influence how search engines perceive the importance of their pages, potentially leading to higher visibility and improved rankings.
3. Indexing of Deeply Buried Pages
Websites with a complex structure or extensive archives may face challenges in getting all their pages indexed. XML sitemaps can address this issue by explicitly listing even the most deeply buried pages within a site. By including these pages in the XML sitemap, website owners increase the chances of search engine crawlers discovering and indexing them, ensuring that valuable content is not overlooked.
4. Quick Identification of Changes
XML sitemaps include the “last modified” tag, which informs search engines about the most recent updates made to a page. This feature is particularly useful for frequently updated content, such as news articles or blog posts. By including this information, website owners can prompt search engines to revisit and reindex their updated pages more promptly, ensuring that the latest content is displayed to users.
5. Facilitating Website Migration and Restructuring
When migrating a website or making significant changes to its structure, it’s essential to guide search engine crawlers through the transition. XML sitemaps can play a crucial role in this process by providing explicit information about the new URLs, redirects, and deprecated pages. By submitting an updated XML sitemap during website migration or restructuring, website owners can help search engines understand the changes, minimizing any negative impact on rankings and visibility.
Best Practices for XML Sitemaps
To maximize the effectiveness of XML sitemaps and further improve your SEO efforts, consider the following best practices:
1. Ensure Comprehensive Coverage
When creating an XML sitemap, it’s crucial to include all relevant pages of your website. This includes not only the main pages but also subpages, blog posts, product listings, and any other content that you want search engines to discover and index. Take the time to regularly update your XML sitemap as you add or remove pages from your site.
2. Prioritize URLs
Assigning priority to URLs within your XML sitemap can provide search engines with additional information about the importance of specific pages. While search engines ultimately determine how to prioritize pages, indicating the relative significance of URLs through priority tags can help guide their crawling and indexing process.
3. Set Frequency of Changes
In the XML sitemap, you can specify the frequency of changes to each page, such as “always,” “hourly,” “daily,” “weekly,” “monthly,” or “yearly.” Providing this information helps search engines understand how often they should revisit and update their index for a particular URL. Be realistic when setting the frequency and ensure it aligns with the actual rate of content updates on your website.
4. Leverage Sitemap Indexing
For larger websites with numerous XML sitemaps, consider utilizing a sitemap index file. A sitemap index acts as a container that references multiple XML sitemap files. This approach is particularly useful for websites with tens of thousands or even millions of pages. By using a sitemap index, you can organize your XML sitemaps effectively and make it easier for search engines to discover and crawl your entire site.
5. Regularly Submit to Search Engines
After creating or updating your XML sitemap, it’s essential to submit it to search engines via their respective webmaster tools. Regularly resubmitting your XML sitemap helps ensure that search engines are aware of any changes and can index your updated content promptly. Additionally, monitoring the indexing status within webmaster tools allows you to identify any errors or issues that may hinder proper crawling and indexing.
Conclusion
XML sitemaps play a critical role in SEO by facilitating efficient crawling, indexing, and visibility of website content. By implementing best practices and creating comprehensive XML sitemaps, website owners can enhance their chances of outranking competitors and achieving better search engine rankings.
Remember that while XML sitemaps are essential, they are just one aspect of a comprehensive SEO strategy. It’s crucial to focus on other key elements, such as creating high-quality content, optimizing on-page elements, and building authoritative backlinks. By combining these strategies and continually refining your SEO efforts, you can position your website for long-term success and increased organic traffic.
Here are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) regarding XML sitemaps and their role in SEO:
Q: What is an XML sitemap?
A: An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the URLs of a website and provides essential information about each page, such as when it was last updated, its priority, and the frequency of changes. It serves as a roadmap for search engine crawlers, helping them discover and index web pages more efficiently.
Q: Why are XML sitemaps important for SEO?
A: XML sitemaps are important for SEO because they improve crawling and indexing, enhance visibility, and ensure that all relevant pages are included in search engine databases. By providing a clear and structured overview of a website’s pages, XML sitemaps enable search engines to navigate and understand the site’s content better.
Q: Do XML sitemaps directly impact search engine rankings?
A: XML sitemaps themselves do not directly impact search engine rankings. However, they facilitate the crawling and indexing process, ensuring that search engines have a comprehensive view of your website’s content. This, in turn, can indirectly influence rankings by improving visibility and ensuring that all relevant pages are included in search engine databases.
Q: How can XML sitemaps help with indexing deeply buried pages?
A: XML sitemaps can help with indexing deeply buried pages by explicitly listing them in the sitemap. Websites with complex structures or extensive archives may have pages that are several levels deep and difficult for search engine crawlers to discover. By including these pages in the XML sitemap, website owners increase the chances of search engine crawlers finding and indexing them.
Q: Should XML sitemaps be submitted to search engines?
A: Yes, XML sitemaps should be submitted to search engines through their respective webmaster tools. By submitting XML sitemaps, website owners alert search engines to changes in their website’s structure or content. This helps search engines crawl and index the updated or new content more efficiently.
Q: Can XML sitemaps improve the indexing of frequently updated content?
A: Yes, XML sitemaps can improve the indexing of frequently updated content. XML sitemaps include the “last modified” tag, which informs search engines about the most recent updates made to a page. By including this information, website owners can prompt search engines to revisit and reindex their updated pages more promptly, ensuring that the latest content is displayed to users.
Q: Are there any best practices for creating XML sitemaps?
A: Yes, there are best practices for creating XML sitemaps, including ensuring comprehensive coverage of all relevant pages, assigning priority to URLs based on their importance, setting the frequency of changes accurately, utilizing sitemap indexing for larger websites, and regularly submitting XML sitemaps to search engines. Validating XML sitemaps and monitoring indexing and crawl errors are also recommended.
Q: Are XML sitemaps the only factor for achieving high search engine rankings?
A: No, XML sitemaps are just one aspect of a comprehensive SEO strategy. While they are crucial for efficient crawling and indexing, other factors such as quality content creation, on-page optimization, building authoritative backlinks, and providing a great user experience also play significant roles in achieving high search engine rankings.
Q: How often should XML sitemaps be updated?
A: XML sitemaps should be updated whenever significant changes are made to your website’s structure or content. This includes adding or removing pages, updating page URLs, or making substantial modifications to existing pages. Regularly updating XML sitemaps ensures that search engines have the most up-to-date information about your website’s pages.
Remember, XML sitemaps are an important tool in your SEO arsenal, but they should be implemented alongside other best practices to achieve optimal results. Continually monitor and refine your SEO strategy to stay ahead of the competition and maintain a strong online presence.